Content
- 1 Understanding Architectural Aluminum Extrusion Profiles in Building Systems
- 2 Role of Aluminum Extrusion Profiles in Facade Systems
- 3 Application of Aluminum Extrusion Profiles in Window Systems
- 4 Use of Aluminum Extrusion Profiles in Door Systems
- 5 Common Profile Features Across Facade, Window, and Door Systems
- 6 Comparison of Profile Requirements by Application
- 7 Why Extrusion Precision Matters in Architectural Systems
Understanding Architectural Aluminum Extrusion Profiles in Building Systems
Architectural aluminum extrusion profiles are engineered aluminum sections designed to serve as functional and structural components in facade, window, and door systems. Through the extrusion process, aluminum billets are shaped into precise cross-sections that support glazing, sealing, load transfer, and assembly requirements in architectural applications. These profiles are developed with building performance, installation accuracy, and system integration in mind rather than generic material use.
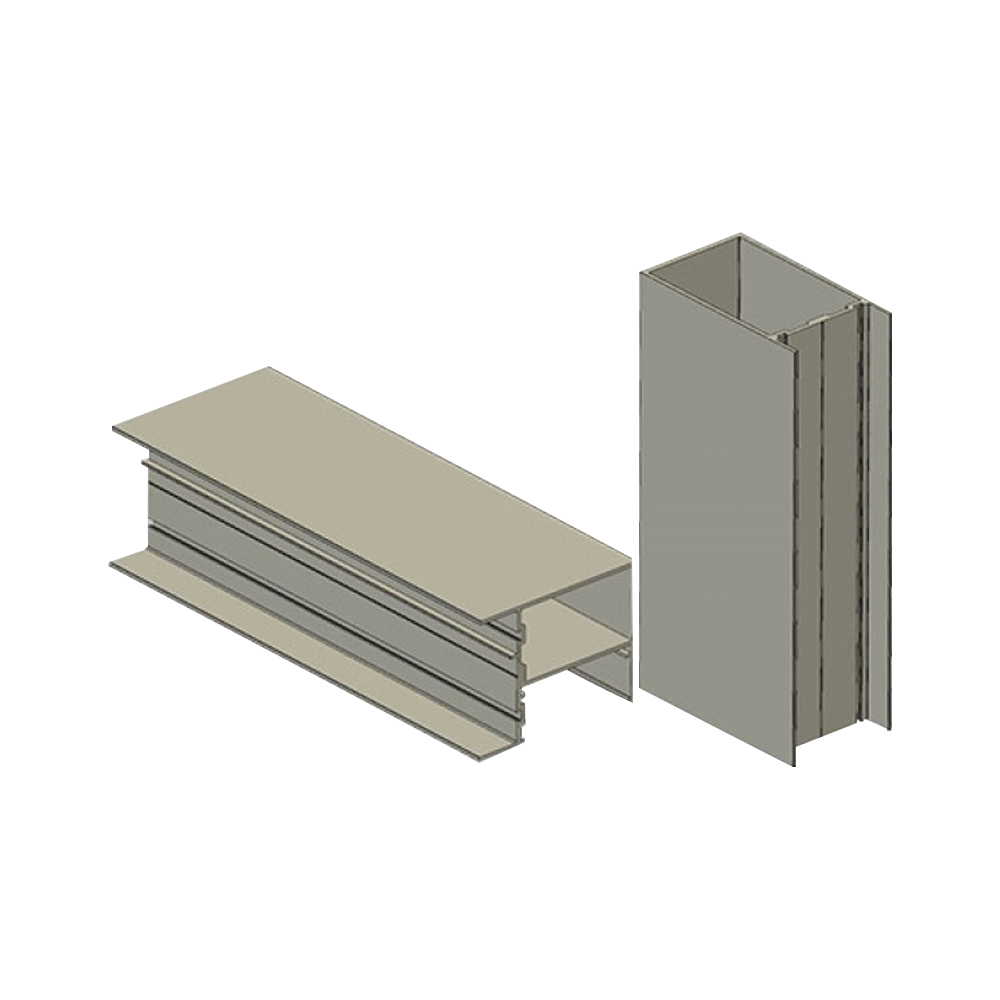
Role of Aluminum Extrusion Profiles in Facade Systems
In facade systems, aluminum extrusion profiles act as the primary framework that connects glass, panels, insulation layers, and structural anchors. Their geometry is designed to manage wind load transfer, thermal movement, drainage paths, and facade alignment. Profiles used in facades are often customized to match curtain wall, unitized facade, or stick system requirements.
Structural Support and Load Distribution
Facade aluminum profiles distribute dead loads and live loads from glazing and panels to the main building structure. Internal ribs, wall thickness, and profile depth are calculated to meet project-specific strength and deflection limits while maintaining a controlled visual width on the exterior.
Drainage and Pressure Equalization Design
Extruded profiles commonly integrate internal drainage chambers, weep paths, and pressure-equalized cavities. These features guide water away from interior spaces and support controlled airflow, which helps manage rain penetration and facade durability over long service cycles.
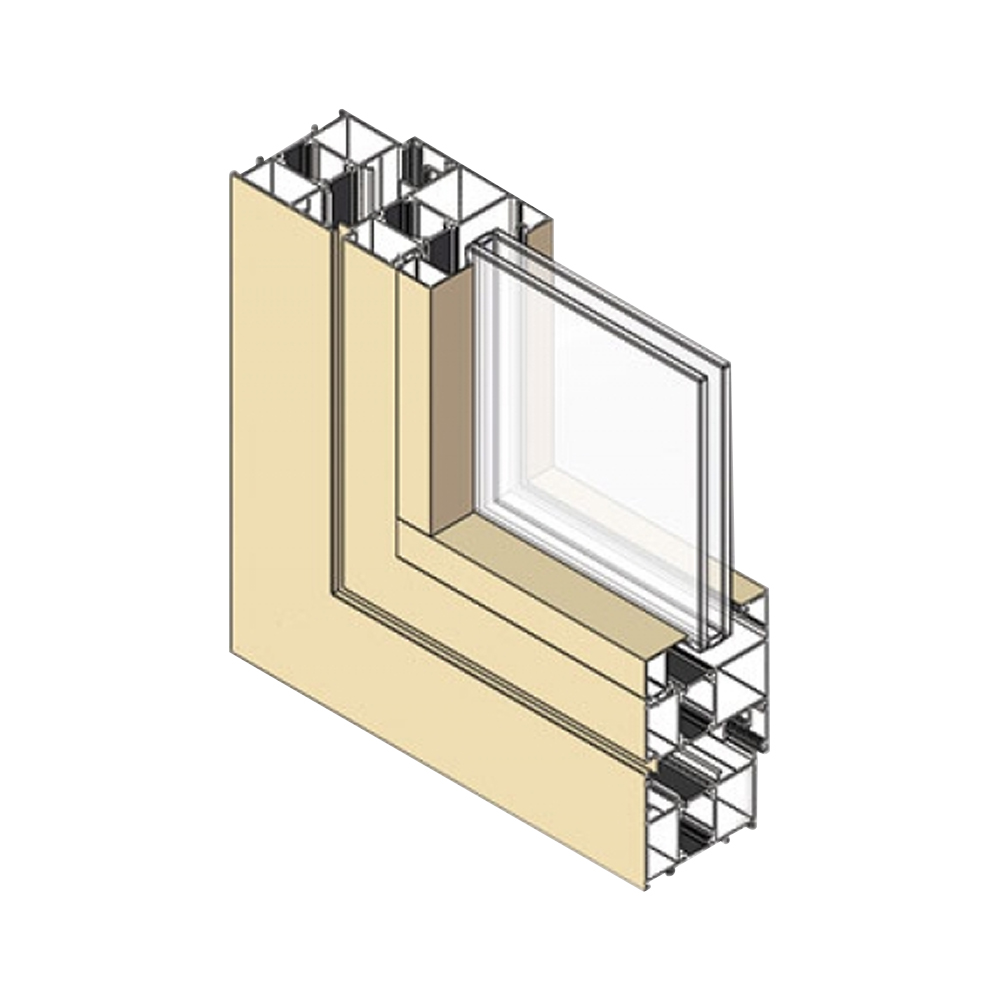
Application of Aluminum Extrusion Profiles in Window Systems
Window systems rely on aluminum extrusion profiles for frames, sashes, mullions, and transoms. Each profile section is designed to support glass thickness, hardware installation, sealing systems, and operational movement. Precision in extrusion geometry directly affects window performance and installation efficiency.
Profile Geometry for Frame and Sash Assembly
Window aluminum profiles feature dedicated grooves and chambers for glazing beads, gaskets, reinforcement inserts, and fastening points. These geometries allow consistent assembly while maintaining tight dimensional tolerances required for smooth opening and closing operations.
Thermal Break Integration in Window Profiles
Many architectural window profiles are designed to accept thermal break strips, separating interior and exterior aluminum sections. The extrusion design accommodates these insulating elements without altering the external appearance, supporting improved thermal performance while preserving structural continuity.
Use of Aluminum Extrusion Profiles in Door Systems
Door systems place higher mechanical and durability demands on aluminum extrusion profiles due to frequent operation and impact loads. Profiles used in doors are typically thicker and reinforced to support hinges, locks, closers, and automatic operation systems.
Profile Design for Hardware Compatibility
Door extrusion profiles include reinforced zones and standardized hardware channels that allow direct installation of locking systems and motion hardware. This integrated approach reduces secondary machining while maintaining alignment accuracy during repeated use.
Sealing and Impact Resistance Considerations
Extruded aluminum door profiles often incorporate multiple sealing grooves to support air and water control. The profile shape also accounts for corner joint strength and resistance to deformation under operational stress.
Common Profile Features Across Facade, Window, and Door Systems
- Integrated channels for gaskets, glazing beads, and sealants
- Reinforcement cavities to increase structural stiffness
- Drainage and ventilation paths formed directly during extrusion
- Standardized connection points for modular system assembly
Comparison of Profile Requirements by Application
| Application Area | Primary Design Focus | Typical Profile Characteristics |
| Facade Systems | Load transfer and weather management | Deep sections, drainage chambers, anchor interfaces |
| Window Systems | Operational precision and sealing | Glazing grooves, thermal break zones, sash profiles |
| Door Systems | Durability and hardware support | Thicker walls, reinforced hardware areas |
Why Extrusion Precision Matters in Architectural Systems
The performance of facade, window, and door systems depends heavily on extrusion precision. Accurate profile dimensions support consistent sealing, predictable load behavior, and smooth installation. Deviations in extrusion geometry can lead to alignment issues, water ingress risks, or reduced system lifespan, making profile design and manufacturing control a central factor in architectural aluminum applications.



 English
English 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어