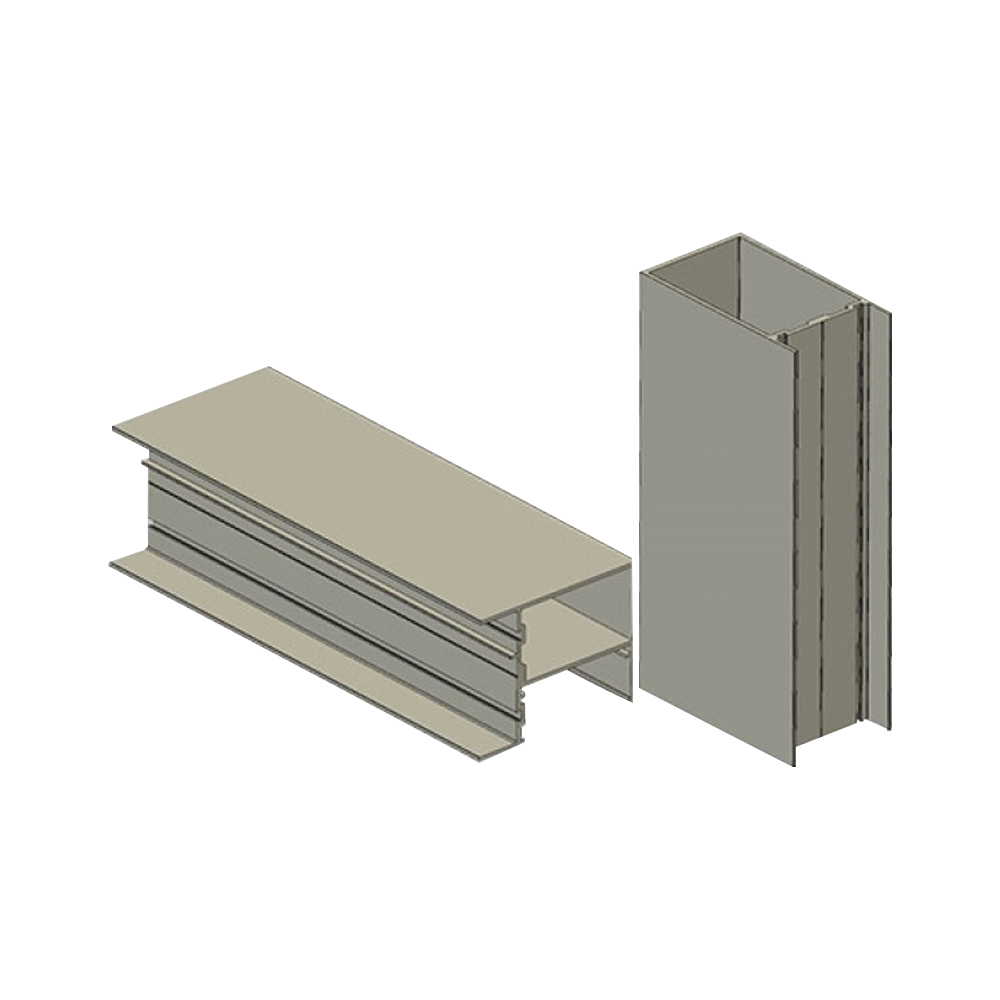
Architectural aluminum extrusion profiles are widely used in modern building systems due to their balance of structural strength, dimensional precision, and surface finish flexibility. These profiles are not only functional structural elements but also visible design components that influence both performance and aesthetics. Understanding how strength, precision, and finish options interact is essential when specifying aluminum extrusion profiles for architectural applications.
This article examines the mechanical characteristics of architectural aluminum extrusion profiles, the factors affecting dimensional accuracy, and the range of surface finishes available for different building requirements. The focus is on practical selection considerations rather than theoretical descriptions.
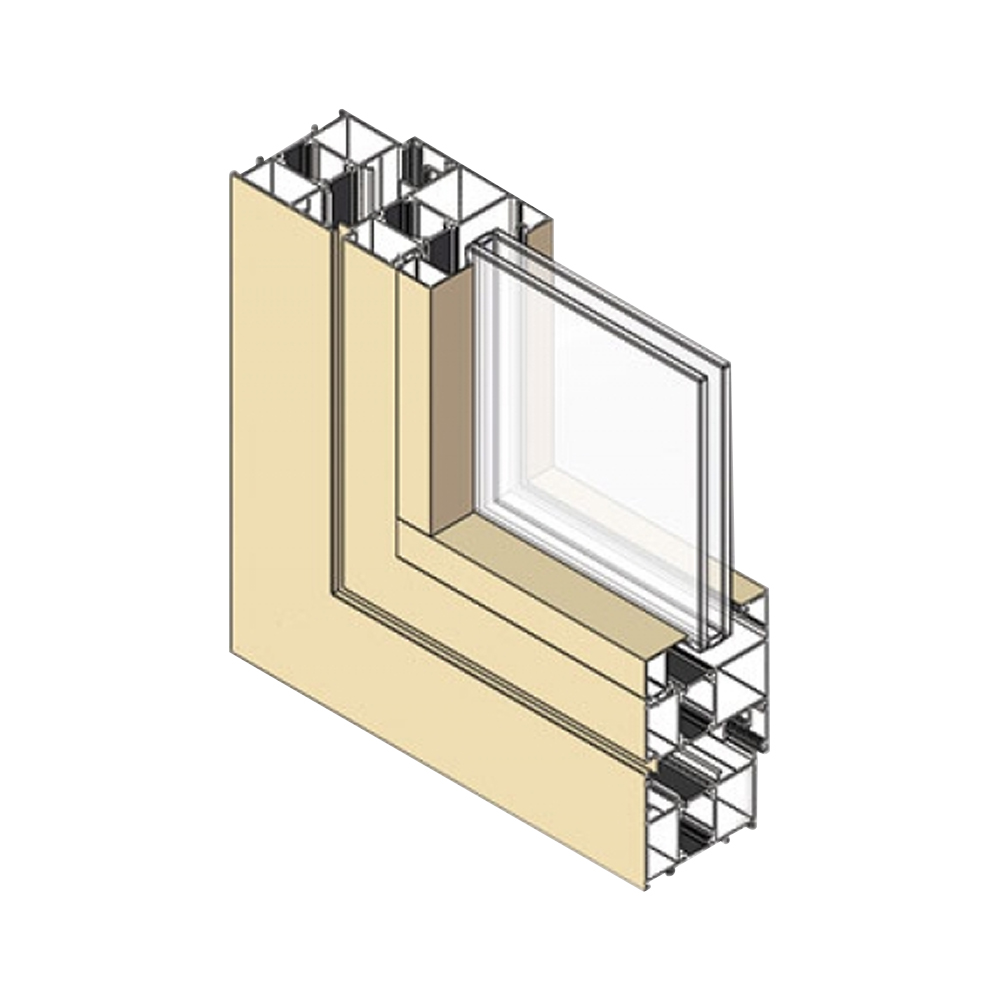
Content
Structural Strength of Architectural Aluminum Extrusion Profiles
Strength is a primary requirement for architectural aluminum extrusion profiles, especially when used in load-bearing or semi-structural applications such as curtain walls, window frames, and support systems. Aluminum alloys commonly used for architectural extrusions are selected to provide sufficient strength while maintaining good formability during the extrusion process.
The structural performance of an extrusion profile depends on both alloy composition and cross-sectional design. Profiles with optimized wall thickness and internal reinforcement features can achieve higher load capacity without excessive material usage. This allows designers to meet structural requirements while controlling overall weight.
Influence of Profile Geometry
Profile geometry plays a critical role in determining strength. Hollow sections, multi-chamber designs, and ribbed structures improve bending resistance and torsional stiffness. These design features are frequently used in architectural aluminum extrusion profiles to enhance performance without increasing external dimensions.
Precision and Dimensional Accuracy in Extrusion Profiles
Precision is a key advantage of architectural aluminum extrusion profiles, particularly in applications requiring tight tolerances and consistent assembly. Accurate dimensions ensure proper fit with glass panels, connectors, fasteners, and sealing components, reducing installation time and adjustment work on site.
Dimensional accuracy is influenced by die design, extrusion parameters, and post-processing operations. Well-controlled extrusion processes help maintain consistent wall thickness, straightness, and surface flatness across production batches.
Tolerance Control and Assembly Compatibility
Tight tolerance control improves compatibility between profiles and system components. This is especially important in modular architectural systems where multiple profiles must align precisely. Reduced dimensional variation contributes to better sealing performance and improved overall system stability.
- Consistent wall thickness across the profile length
- Controlled straightness and minimal twisting
- Accurate slot and groove dimensions for accessories
Finish Options for Architectural Aluminum Extrusion Profiles
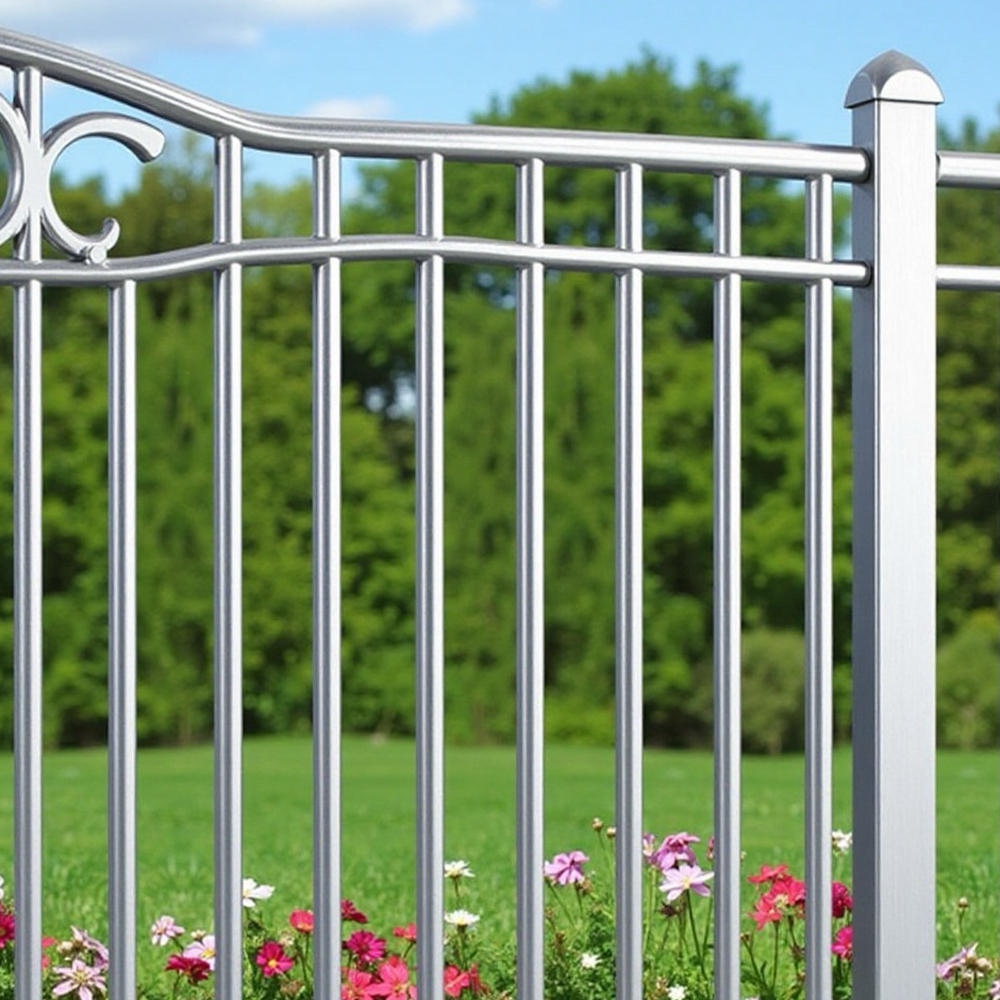
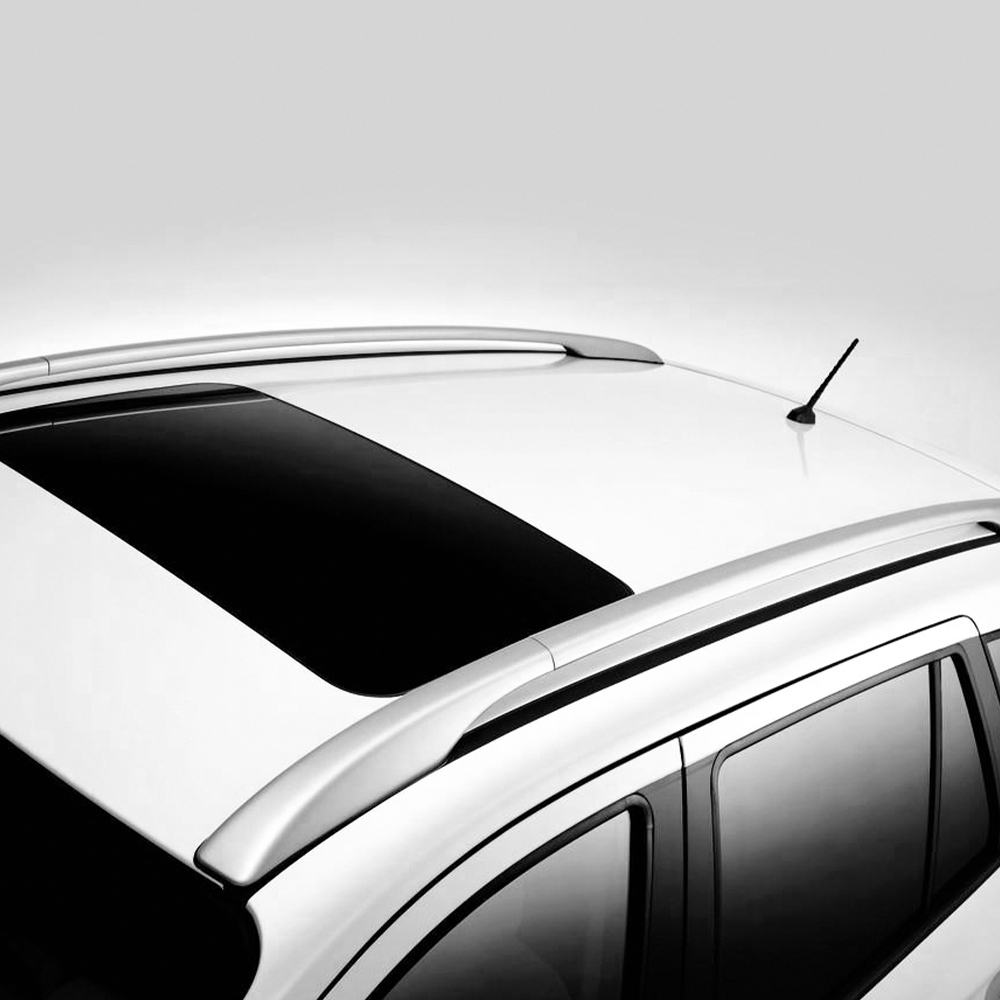
Surface finish options are a defining feature of architectural aluminum extrusion profiles. Finishes affect not only visual appearance but also corrosion resistance, wear performance, and maintenance requirements. The selection of an appropriate finish depends on environmental exposure, design intent, and expected service life.
Common finish processes include anodizing, powder coating, and mechanical surface treatments. Each option offers distinct performance characteristics and aesthetic possibilities.
Common Surface Treatment Methods
| Finish Type | Primary Function | Typical Application |
| Anodized Finish | Corrosion resistance and surface hardness | Curtain walls and window frames |
| Powder Coated Finish | Color consistency and weather protection | Exterior architectural elements |
| Mill Finish | Natural aluminum appearance | Non-visible structural components |
Balancing Strength, Precision, and Finish Selection
In architectural applications, strength, precision, and finish selection must be considered together rather than independently. A profile with excellent structural properties but poor dimensional accuracy may lead to installation issues. Similarly, a visually appealing finish may not perform well if the underlying profile lacks sufficient strength.
Effective specification of architectural aluminum extrusion profiles involves matching mechanical performance with manufacturing capability and surface treatment requirements. This integrated approach helps achieve reliable performance throughout the lifecycle of the building system.
Conclusion
Strength, precision, and finish options are core factors that define the performance and suitability of architectural aluminum extrusion profiles. By understanding how alloy selection, profile design, tolerance control, and surface treatment interact, designers and engineers can specify profiles that meet both structural and aesthetic requirements. Careful consideration of these elements supports consistent quality, efficient installation, and long-term durability in architectural applications.



 English
English 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어