Content
- 1 Role of Automotive Aluminum Extrusion Profiles in Vehicle Design
- 2 Common Automotive Applications of Aluminum Extrusion Profiles
- 3 Material Selection for Automotive Aluminum Extrusions
- 4 Design Considerations for Automotive Extrusion Profiles
- 5 Manufacturing Process of Automotive Aluminum Extrusion Profiles
- 6 Surface Treatment and Corrosion Protection
- 7 Quality Control and Automotive Standards
- 8 Future Development Trends in Automotive Aluminum Extrusions
Role of Automotive Aluminum Extrusion Profiles in Vehicle Design
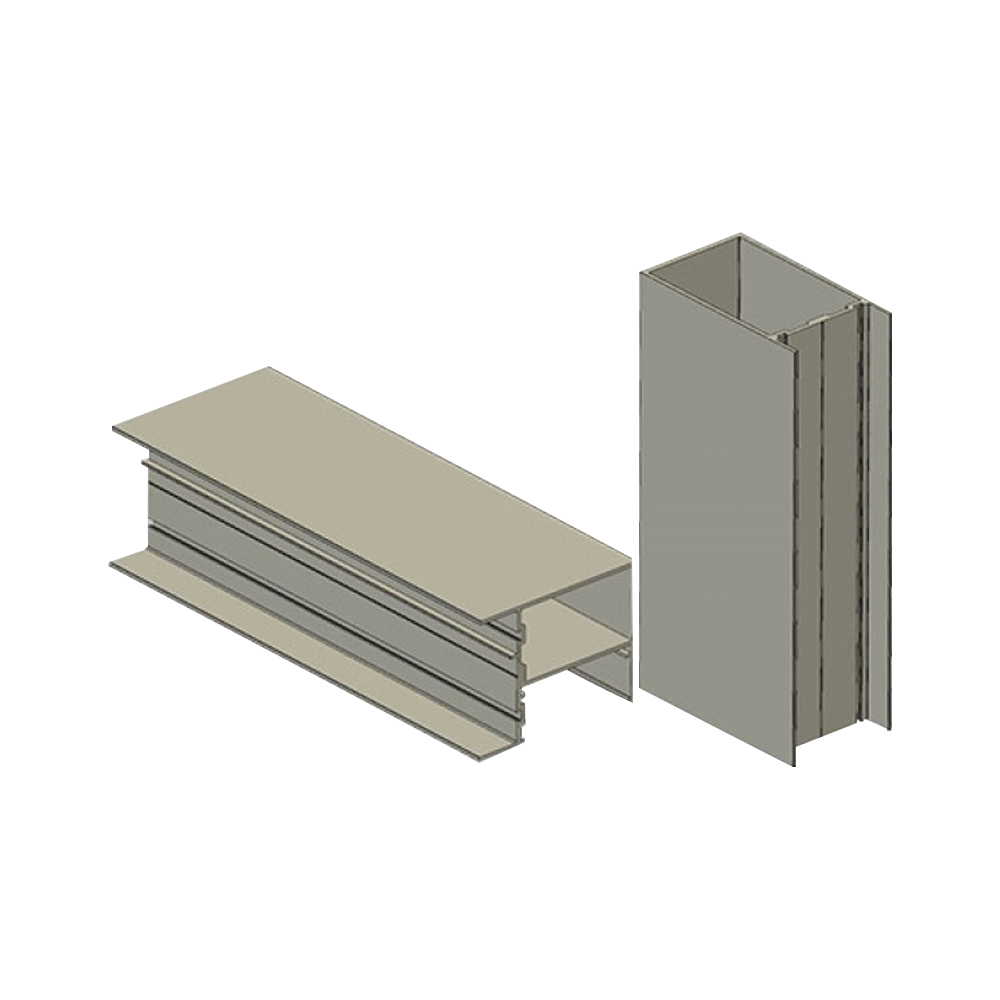
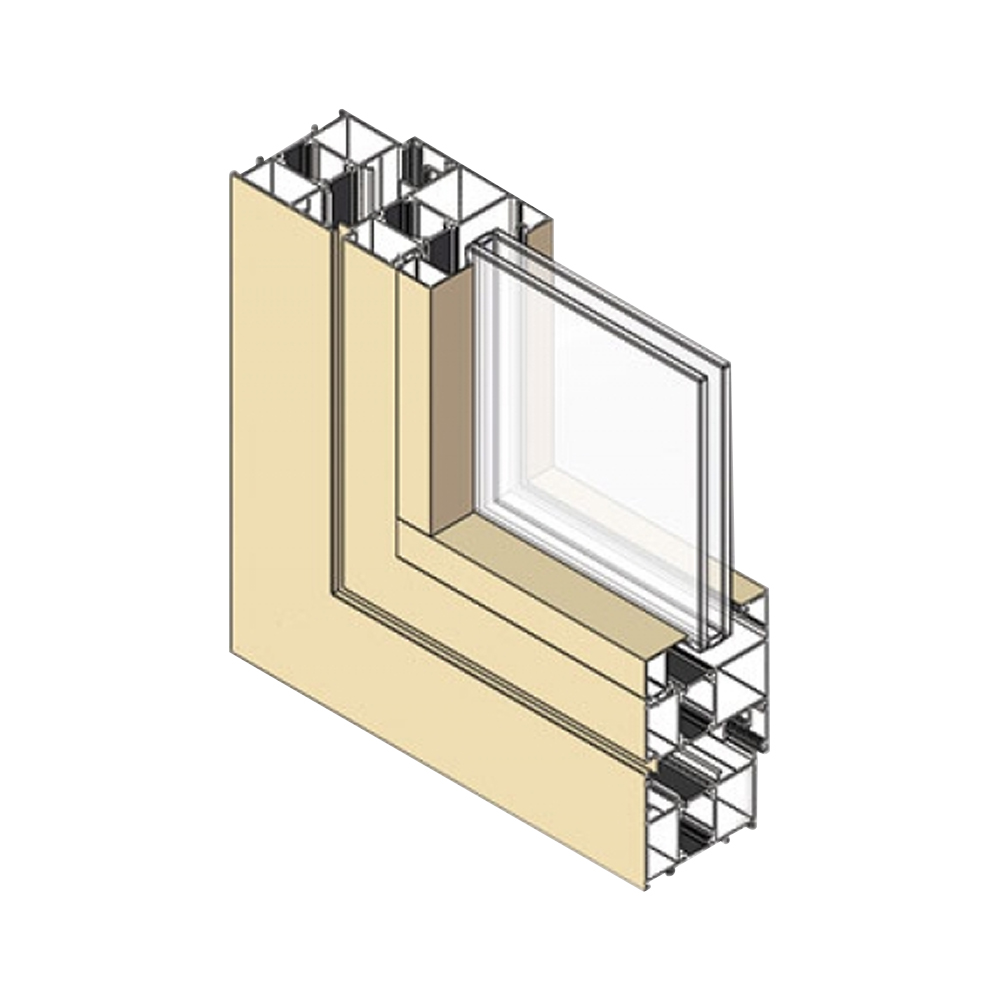
Automotive aluminum extrusion profiles are structural and functional components formed by forcing aluminum alloy billets through precision dies. In modern vehicle engineering, these profiles are widely used to replace traditional steel parts in order to reduce vehicle weight, improve energy efficiency, and support complex structural integration. Compared with stamped components, extruded profiles allow designers to combine multiple functions into a single section, reducing part count and assembly complexity.
In passenger cars, commercial vehicles, and new energy vehicles, extrusion profiles are applied in load-bearing frames, safety structures, and auxiliary systems. Their consistent cross-section, controllable wall thickness, and adaptability to different joining methods make them suitable for both mass production and customized platforms.
Common Automotive Applications of Aluminum Extrusion Profiles
Automotive aluminum extrusion profiles are selected based on mechanical performance, dimensional accuracy, and integration requirements. Different vehicle systems rely on specific profile designs to meet strength, stiffness, and durability targets.
- Battery pack frames and trays for electric vehicles, providing structural support and heat dissipation paths
- Crash management systems such as bumper beams and crash boxes designed for controlled energy absorption
- Side sills, roof rails, and longitudinal beams contributing to body-in-white stiffness
- Seat tracks, roof racks, and interior structural supports requiring dimensional stability
- Cooling system frames and electronic housing structures with integrated channels
Material Selection for Automotive Aluminum Extrusions
The performance of automotive aluminum extrusion profiles depends heavily on alloy selection and temper condition. Automotive manufacturers typically choose alloys that balance strength, formability, corrosion resistance, and cost.
Typical Aluminum Alloys Used
| Alloy Series | Key Characteristics | Automotive Usage |
| 6000 Series | Good strength, corrosion resistance, heat-treatable | Structural frames, battery enclosures |
| 7000 Series | High strength, lower formability | Reinforcement parts, crash components |
Design Considerations for Automotive Extrusion Profiles
Designing automotive aluminum extrusion profiles requires coordination between vehicle engineers, extrusion manufacturers, and tooling specialists. Section geometry directly affects strength, torsional rigidity, and manufacturability.
Engineers often incorporate hollow chambers, internal ribs, and variable wall thickness to optimize material distribution. These features help achieve stiffness targets while limiting overall mass. Radii, corner thickness, and symmetry are also carefully controlled to maintain stable metal flow during extrusion.
Functional Integration in Profile Design
- Cable routing channels integrated into the profile cross-section
- Mounting grooves for fasteners, seals, or plastic covers
- Drainage and ventilation paths for moisture management
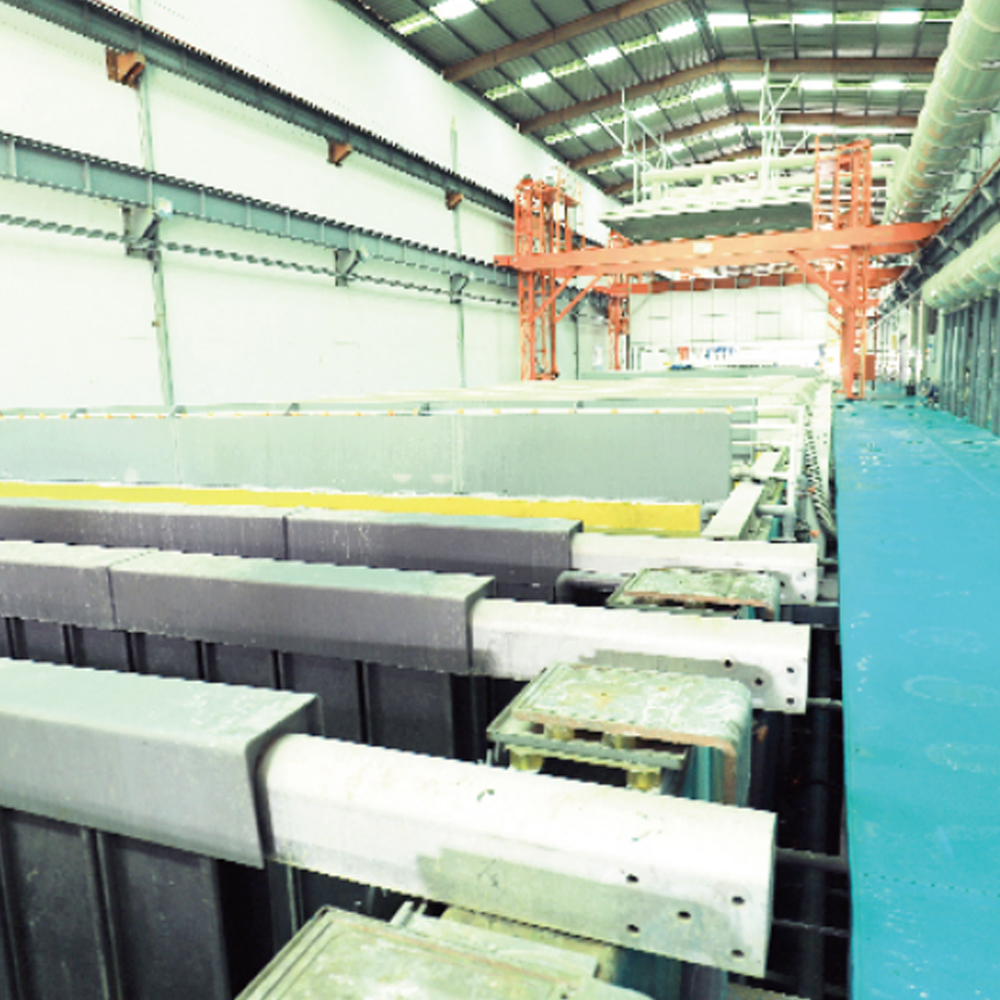
Manufacturing Process of Automotive Aluminum Extrusion Profiles
The manufacturing process starts with aluminum billet heating, followed by extrusion through a custom-designed die. After extrusion, profiles undergo quenching, stretching, and aging to reach specified mechanical properties. Dimensional consistency is maintained through controlled process parameters and online monitoring.
Post-extrusion operations such as cutting, CNC machining, punching, and bending are commonly applied to meet assembly requirements. For automotive use, tight tolerances and repeatability are critical, especially for automated welding and robotic assembly lines.
Surface Treatment and Corrosion Protection
Automotive aluminum extrusion profiles often receive surface treatments to improve corrosion resistance, appearance, and bonding performance. The selected treatment depends on the installation environment and downstream processes.
- Anodizing for enhanced corrosion resistance and surface hardness
- Powder coating for aesthetic consistency and environmental protection
- Pre-treatment layers compatible with adhesive bonding and painting
Quality Control and Automotive Standards
Automotive aluminum extrusion profiles are produced under strict quality management systems. Dimensional inspections, mechanical testing, and surface evaluations are conducted throughout production. Traceability of raw materials and process parameters is maintained to support automotive supply chain requirements.
Profiles supplied to automotive projects typically comply with international standards and OEM-specific specifications. Consistency in batch performance is essential for ensuring assembly accuracy, structural reliability, and long-term vehicle performance.
Future Development Trends in Automotive Aluminum Extrusions
As vehicle electrification and lightweight design continue to advance, automotive aluminum extrusion profiles are evolving toward higher integration and structural efficiency. Large cross-section profiles, multi-cavity designs, and hybrid structures combining extrusion with casting or sheet components are becoming more common.
These developments support flexible vehicle platforms and modular architectures, enabling manufacturers to adapt quickly to different models and market demands while maintaining consistent production quality.



 English
English 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어